Mga spotlight
Agricultural Systems Specialist, Conservation Engineer, Engineer, Product Engineer, Product Technology Scientist, Project Engineer, Research Agricultural Engineer
Agriculture is a trillion-dollar business and a huge part of our nation’s economy. It’s also much more complex than most people realize. There are numerous machines, equipment, power supplies, irrigation systems, and facilities to take care of, requiring the skills of an Agricultural Engineer.
Agricultural Engineers apply engineering principles to improve the sustainability and productivity of processes, equipment, and systems. This includes environmental management, to reduce pollution and harmful effects on ecosystems. They also help integrate automation and robotics into agribusiness operations, study soil fertility and nutrient content, estimate potential crop yields, and optimize food processing methods.
In short, though they work in a relatively small career field, their insights, knowledge, skills, and services are invaluable to society!
- Improving agribusiness processes to benefit owners, consumers, and the environment
- Being part of a massive sector that’s vital to the economy and the food supply chain
- Nagtatrabaho sa isang kumikita, dalubhasang angkop na lugar na may magagandang pagkakataon sa karera
- Nakakaapekto sa kalusugan ng pananalapi at katatagan ng mga komunidad sa kanayunan
Oras ng trabaho
- Agricultural Engineers work full-time jobs, typically with nights, weekends, and holidays off. Overtime may be needed to meet deadlines. Occasional travel and exposure to inclement weather may be necessary.
Mga Karaniwang Tungkulin
- Work with farmers, seafood farmers, forestry professionals, and food processing teams on various projects
- Meet with employers, clients, contractors, developers, city representatives, and fellow engineers to review projects, goals, timeframes, and costs
- Create proposals, presentations, graphics, budgets, and reports for projects
- Use computer-aided drafting programs to design agricultural equipment, irrigation systems, climate control systems, facilities, sensor devices, layouts, parts, etc.
- Work with artificial intelligence and geospatial systems to improve and automate processes
- Design methods to alter and maximize where sun, rain, and wind affect fields and structures
- Assist with creating more efficient climate control and refrigeration systems, facilities for food and crop processing and storage, animal housing, land reclamation projects, and more
- Provide guidance and oversight for new construction projects (such as electric-power distribution systems, irrigation, or flood control systems), new mechanical systems, or production plant operations
- Offer expert advice regarding water quality issues, pollution management, and resource utilization
Karagdagang Pananagutan
- Quality test machines and equipment for performance and safety
- Conduct site visits and offer consultations
- Train and mentor team members, as needed
- Panatilihin ang magandang relasyon sa mga lokal na magsasaka, may-ari ng agribusiness, asosasyon sa industriya, at mga kaugnay na organisasyon o ahensya
- Create or present educational materials to farmers or farm co-ops to enhance sustainability
- Research and develop new technologies and potential capabilities
- Stay up to date on manufacturers’ manuals, federal and state regulations, industry changes, and technological advancements
- Dumalo sa mga kaganapan ng propesyonal na organisasyon upang magbahagi ng impormasyon at matuto mula sa iba
Soft Skills
- Koordinasyon ng mga Aktibidad
- Analitikal
- Pansin sa detalye
- Katalinuhan sa negosyo
- Pakikipagtulungan
- Pagkamalikhain
- Kritikal na pag-iisip
- mapagpasyahan
- Deduktibo at pasaklaw na pangangatwiran
- Mabusisi pagdating sa detalye
- Independent
- Pagsubaybay
- Layunin
- Organisado
- pasyente
- Perceptive
- Pagtugon sa suliranin
- Pag-unawa sa pagbasa
- Nakatuon sa kaligtasan
- Malakas na kasanayan sa komunikasyon
- Visualization
Teknikal na kasanayan
- Computer-aided na disenyo
- Engineering at teknolohiya
- Familiarity with applicable federal and state regulations
- Knowledge of fabrication and manufacturing
- Kaalaman sa sektor ng agrikultura
- Kakayahang mekanikal
- Pagsusuri ng operasyon
- Risk assessment principles
- Strong science and math skills
- Mga ahensya ng gobyerno
- Institusyong pang-edukasyon
- Consulting service and engineering agencies
The work of Agricultural Engineers is vital for helping agribusinesses improve efficiency and become more sustainable. The national economy—and all food consumers—depend greatly on the success of such businesses.
Surrounding rural communities are also deeply affected by how well local farms and agribusinesses are doing. Meanwhile, local citizens in general often take a keen interest in environmental and food safety issues. Suffice it to say, Agricultural Engineers carry a lot of responsibility on their shoulders!
The agricultural sector is continuously impacted by climate and environmental factors that affect crop production, exacerbate costs, and may result in economic losses. Agricultural Engineers do their best to assist these businesses as they try to adapt to changes. Part of this includes helping them be more “climate-smart” by incorporating sustainable, environmentally-friendly equipment, machines, systems, and processes.
Agricultural Engineers assist with designing and adopting automation and robotics technologies; leveraging the power of data-gathering sensors and the Internet of Things; creating more climate-resilient infrastructures and better water management strategies; helping build robust food safety protocols; and devising strategies to reduce waste and create circular economies.
Agricultural Engineers may have shown early interest in science, nature, plants and animals, or building and tinkering with things. Many grow up in rural areas and are exposed to farming and gardening at a young age. Others simply love STEM-related activities and want to apply what they learn to improve the world around them!
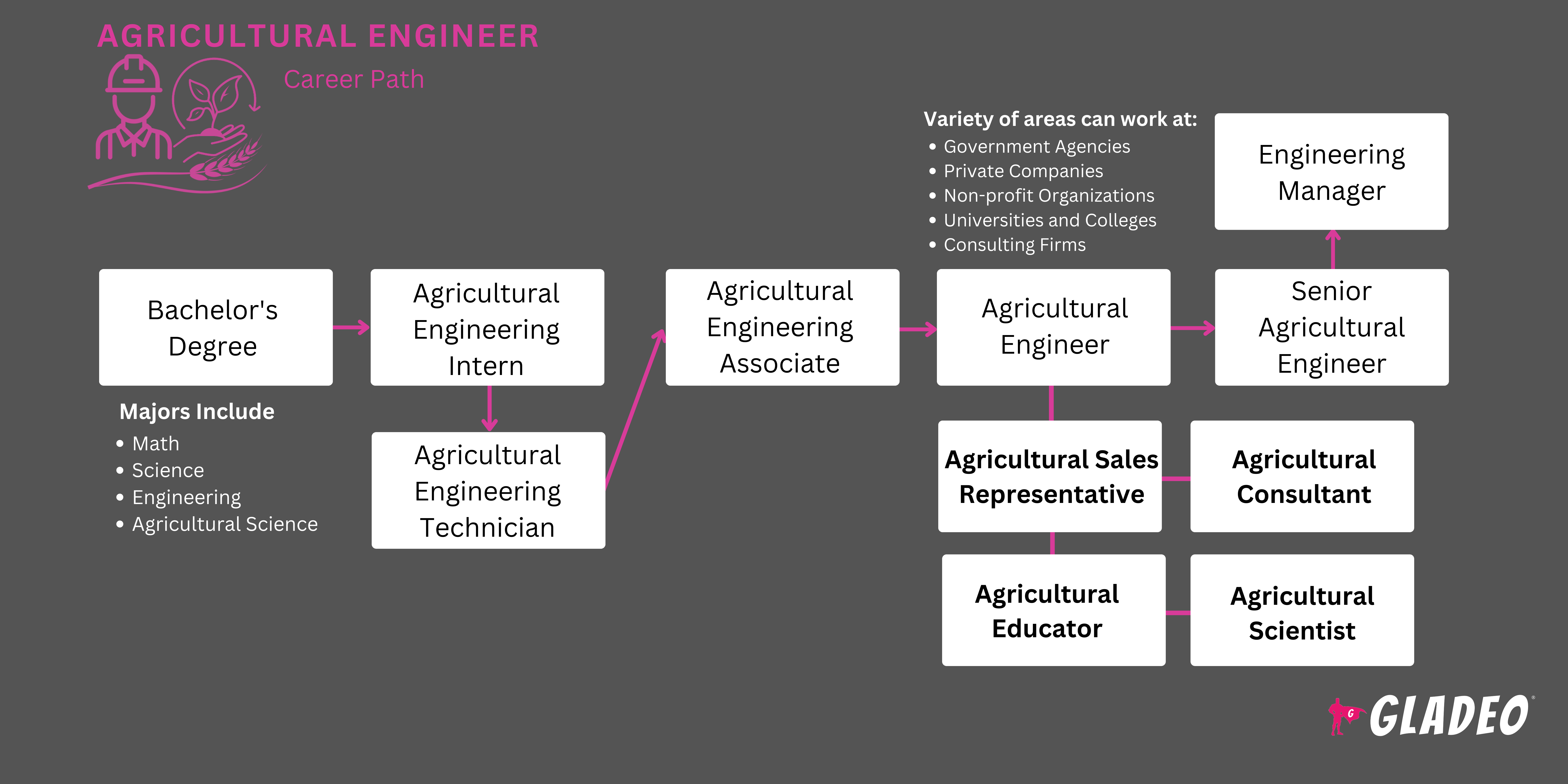
- Agricultural Engineers generally need an ABET-accredited bachelor’s in agricultural engineering, agriculture, agricultural operations, biological engineering, or related fields
- Maraming mga mag-aaral ang nagpasyang magtapos ng dalawahang bachelor's/master's na makakatipid ng oras at pera
- Maaaring hindi kailangan ng master ngunit maaari kang gawing mas mapagkumpitensya at maaaring maging kwalipikado ka para sa mas mataas na panimulang suweldo o posisyon
- Common master’s degrees for this field include a Master of Science in Agriculture or a Master of Engineering
- Per O*Net, 69% of workers in this field have a bachelor’s, 12% have a post-baccalaureate certificate, and 12% have a master’s
- A lot of college programs partner with local businesses to offer internships and cooperative experiences to develop practical skills
- Students should gain a strong understanding of the agriculture sector and the variables which impact it
- Common college courses include:
- Agricultural Electronics and Control
- Agri-Industrial Applications of Electricity
- Farm Tractors and Power Units
- Food Process Engineering Technology
- Geographic Information Systems for Resource Management
- IT for Agricultural Systems
- Management of Agricultural Systems
- Processing and Storage of Agricultural Products
- Spatial Technology for Precision Agriculture
- Technology for Environmental and Natural Resource Engineering
- Water and Soil Management
- Kasama sa mga opsyonal na sertipikasyon ang:
- American Society for Quality’s Certified Reliability Engineer
- American Society of Agronomy’s Certified Crop Advisor and Certified Professional Agronomist
- American Society of Farm Managers and Rural Appraisers’ Accredited Agricultural Consultant
- Irrigation Association’s Certified Irrigation Designer - Landscape
- Hindi kailangan ng lisensya para makapagsimula, ngunit may mga opsyon sa paglilisensya ng estado na isasaalang-alang sa ibang pagkakataon sa karera ng isang tao
- Professional Engineering (PE) licensure leads to greater scopes of responsibility
- Ang PE ay dapat pumasa sa dalawang pagsusulit:
- Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) - to be certified as an Engineer in Training (EIT) or an Engineer Intern (EI)
- Principles and Practice of Engineering (PE) exam
- Students should seek colleges offering majors in agricultural or biological engineering
- Maghanap ng mga programa na may mga internship o iba pang mga pagkakataon kung saan maaari kang makakuha ng praktikal na karanasan, lalo na nauugnay sa pamamahala ng kredito sa agrikultura
- Palaging ihambing ang mga gastos sa matrikula at iba pang mga bayarin. Suriin ang iyong mga opsyon para sa mga scholarship at tulong pinansyal
- Tingnan kung ang programa ay may anumang pakikipagsosyo sa mga kumpanyang kumukuha ng mga nagtapos!
- Tandaan ang mga istatistika ng pagtatapos at paglalagay ng trabaho para sa mga alumni
- Sign up for HS classes in biology, chemistry, physics, advanced math (algebra, geometry, trigonometry, and calculus), environmental studies, computer programming, drafting, business, shop, and writing
- Ask a teacher or counselor about school-related agriculture programs you can participate in
- Magboluntaryo para sa mga aktibidad sa paaralan kung saan matututong magtrabaho nang epektibo bilang isang pangkat at pamahalaan ang mga proyekto
- Maghanap ng mga internship, karanasan sa kooperatiba, o part-time na trabaho habang nasa kolehiyo
- Write down the names and contact info of people who can serve as job references
- Study books, articles, and video tutorials related to different aspects of Agricultural Engineering. Think about any areas you might want to specialize in!
- Start drafting your resume early and keep adding to it as you go, so you don’t lose track
- Consider doing ad hoc courses via Coursera or other sites to learn more about agribusiness
- Request an informational interview with a working Agricultural Engineer
- Sumali sa mga propesyonal na organisasyon upang matuto, magbahagi, makipagkaibigan, at mapalago ang iyong network (tingnan ang aming listahan ng Mga Mapagkukunan > Mga Website )
- Tingnan ang mga portal ng trabaho tulad ng Indeed.com , LinkedIn , Glassdoor , Monster , CareerBuilder , SimplyHired , o ZipRecruiter
- Also look at AgCareers, AgHires, Farm Job Search, EcoFarm, Farm and Ranch Jobs, USDA Jobs, and related sites
- Consider relocating to a rural area where there are farms and agribusinesses
- Let your network know you’re looking for work. Most jobs are still found through personal connections—plus, this is not a big career field!
- Tanungin ang iyong mga instruktor, dating superbisor, at/o mga katrabaho kung handa silang magsilbi bilang mga personal na sanggunian. Huwag ibigay ang kanilang personal na impormasyon sa pakikipag-ugnayan nang walang paunang pahintulot
- Check out some Agricultural Engineer resume examples and sample interview questions such as “Which techniques have you used to extract toxic elements from the soil?” or “How do you communicate with stakeholders to change perspectives on organic varieties of existing crops?”
- Magsanay sa paggawa ng mga kunwaring panayam sa career center ng iyong paaralan (kung mayroon sila nito)
- Magsuot ng angkop para sa mga panayam at ipakita ang iyong sigasig para sa at kaalaman sa larangan
- Communicate regularly with leadership and stakeholders to ensure objectives and timeframes are clearly defined and achievable. Don’t make promises you can’t keep!
- Use your industry knowledge to anticipate and mitigate issues before they become problems
- Speak with colleagues working in other agribusinesses to exchange information and tips (when possible. Some information may be proprietary or otherwise restricted)
- Solve tough challenges for your employer. Add tangible value by boosting efficiency, productivity, and sustainability
- Have a contingency plan to respond to critical issues quickly and decisively
- Study trends and advances in applicable technologies, equipment, and processes
- Participate in professional organizations like the American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers. Keep learning and expanding your knowledge base and skills
- Mabisang makipagtulungan sa mga miyembro ng koponan at bumuo ng matibay na relasyon sa mga lokal na magsasaka, may-ari ng agribusiness, at iba pang stakeholder sa komunidad
- Don’t be shy! Speak with your boss about career progression
- Knock out a specialty certification such as the American Society for Quality’s Certified Reliability Engineer or the American Society of Agronomy’s Certified Crop Advisor and Certified Professional Agronomist
- Complete a graduate degree such as a Master of Science in Agriculture or a Master of Engineering
- Earn your Professional Engineering license
- Consider applying to work for a larger organization with more advancement opportunities
Mga website
- ABET
- American Geophysical Union
- American Society for Engineering Education
- American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers
- American Society of Agronomi
- American Society of Civil Engineers
- American Society of Irrigation Consultant
- Asosasyon para sa Internasyonal na Agrikultura at Pag-unlad sa Rural
- Hinaharap na Magsasaka ng Amerika
- Samahan ng Patubig
- Journal ng Agricultural Engineering
- National Council of Examiners for Engineering and Surveying
- National Institute for Certification in Engineering Technologies
- National Institute of Food and Agriculture, U.S. Department of Agriculture
- Pambansang Lipunan ng mga Propesyonal na Inhinyero
- US Food and Drug Administration
Mga libro
- Agricultural Engineering and Feeding the Future, by Anne Rooney
- Introduction to Agricultural Engineering Technology: A Problem-Solving Approach, by Harry L. Field and John M. Long
- Rainwater Harvesting For Irrigation: Discover Everything You Need to Master Rainwater Harvesting in Your Garden or Farm, by Melanie Davis
Agricultural Engineering is a vital but relatively small field. The current job outlook from the Bureau of Labor Statistics does not suggest much growth in the coming years. This means that to find work, you may have to wait for a currently-working Agricultural Engineer to retire!
If you’re curious about related career options, consider the below similar occupations:
- Agricultural or Food Scientist
- Tagapamahala ng Arkitektural at Inhinyero
- Biofuels Production Manager
- Inhinyerong sibil
- Conservation Scientist
- Inhinyero sa Kapaligiran
- Farmer/Rancher
- Hydrologist
- Industrial Engineer
- Mechanical Engineer
Newsfeed
Mga Tampok na Trabaho

Mga Online na Kurso at Tool








